Table of Contents
Apart from price, internet speed is an essential factor that consumers consider when looking for internet providers. While the price is straightforward, download speed isn’t so here we wanted to offer this easy-to-follow article about internet speeds explained.
Key Takeaways
- Broadband speeds are measured in megabits per second, often shortened to Mbps. The higher the number of Mbps you have, the speedier your online activity should be.
- 100 Mbps is great for multiple users or devices, but it’ll get even better as you keep adding Mbps. When you get to the 500 to 1000 Mbps range, you could basically do anything on multiple devices with lightning fast speed
- There are a number of factors that can affect Internet speeds or your connection to the Internet.
The download and upload speeds goes beyond knowing the monthly charges and fitting it into your budget for your target high speed internet plan. With all the talks surrounding gigabit, broadband, fiber, and megabits, it is easy to be overwhelmed. Sometimes 100 Mbps download speed is fast enough, while in other cases, it is regarded as slow internet connection speed. Throttled internet is a thing that's often overlooked with internet service providers.
We have created this piece to give you a clear understanding of what internet speed entails. The review covers the meaning of internet connection speed, which is considered fast internet, and how to determine the right rate for you. So, what is a good internet speed?
Let’s dig in!
What Is Internet Speed, and Why Does it Matter?
Internet speed is a lot like water pressure; it’s about the volume of moving water at a given time. A computer that is connected to the internet receives information from another through electronic packets. A packet refers to a unit of data. When many packs are delivering data at the moment, the volume of data will be high, and so the internet speed will be fast.
Consider the analogy of a showerhead. When only a little water is trickling out, it may take you forever to rinse out the shampoo. On the other hand, water that is coming out with high pressure makes it easy to clean your hair. Internet speed works in the same way. Slow speed means that you won’t stream a video without buffering. Nobody wants that, which is why the demand for faster WiFi speed is high because it ensures a smooth internet experience.
How to Measure Internet Speed
In the simplest terms, internet speeds are measured by how quickly you can download or upload content in a second and the most used term is megabits per second (mbps). For many people, download speed matters more than the upload rate. That is because you download a lot of things like music, streaming shows, browsing online and online gaming. Upload speed comes in when you send or upload large files or hold video conferencing or video calls. In addition, follow this link if you need upload for gaming most of the time.
Both upload and download speeds are measured in bits per second. Due to the nature of large upload files, we tend to stick to prefixes like G, M, and K to tell how many thousands of megabits that one is referring to. The most used designation is Mbps because it is more relevant to what many people use the internet for. Internet speed could also fall into the ranges of kbps, but those are what we know to be slow internet connections. Gbps refers to high speed internet connection, which is rare but is slowly becoming more prevalent than in the past.
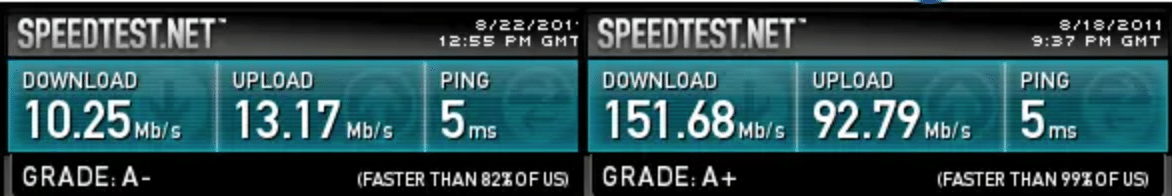
You can use a free speed test such as at speedtest.net to measure your internet speed or how much internet speed you are getting from your internet provider. Also, make sure no other devices or people use the broadband connection during the speed test.
Is broadband the “National Speed Limit”?
Regulations on internet speeds are relatively new, but many governments are choosing to regulate the internet speeds too. Some recommend that the minimum download should be 25Mbps with a minimum upload speed of 3Mbps. That is a fair baseline to determine fast and slow speeds. Those that a have faster internet connection than the standard broadband are considered fast internet, while those below the bandwidth are deemed slow. Besides what the broadband internet providers offer, other factors affect the actual performance, and factors affect internet speeds. Using the connection speeds for demanding tasks like downloading HD video or streaming in 4K can strain even the highest rates.
Types of Internet and How They Affect the Speed
1. Fiber
Reasonable mbps for fiber - 5 to 10 Mbps
It is the fastest internet technology available today. To transfer data, it utilizes fiber-optic cables that can transmit large amounts of information fast. Although it is quick, fiber is not as accessible in most parts of the world compared to other technologies. The biggest hindrance to its development is the high cost of building the required infrastructure. You can find fiber broadband availability in your area here.
2. Satellite

Reasonable mbps for satellite - 12 to 100 Mbps
Want to know how satellite internet works? Consumers access the internet wirelessly from the receiver. However, they must involve wires to transport the signal from the receiver to various locations in the building. Since it is wireless, satellite internet is widely available. Its bandwidth is closer to that of DSL but is often has slower speeds because of dormancy.
3. Cable
Reasonable mbps for cable – 10 Mbps to 1,000 Mbps
Here, the internet is transported through similar cables to those that are used to transmit TV services. Cable internet has a high broadband internet capacity to attain high speed internet connection. Its speeds are often faster than DSL.
4. DSL
Reasonable mbps for DSL - 3 Mbps to 115 Mbps
It stands for Digital Subscriber Line. The connection is similar to a regular phone line, but it has advanced wiring that enables broadband connection. Therefore, DSL is faster than dial-up. Most telephone companies, both current and former, usually offer internet services using this technology and are available in many service areas.
5. Dial-up
Reasonable mbps for dial-up - 56 Kbps
It is the slowest connection technology since it can’t support broadband. Therefore, dial-up often has limited bandwidth. Because of these shortcomings, it is outdated and doesn't exist in most first world countries. It's the first internet connection that was popularized and would often be interrupted by phone calls.
What Affects my Internet Speed?
- Traffic congestion – Sadly enough, your internet might also encounter congestion. Picture how busy a freeway gets on a regular evening. The more the data transfer you request at a time, the more the bandwidth that is required, and consequently, the slower the download or upload speeds. Congestion usually occurs during peak time, such as when everyone has just gotten home from work or during the weekends.
- Your location – if you reside in a busy city or town, you are likely to have internet access to a variety of internet types. People living in cities usually have higher broadband speeds than those in rural areas.
- Connection type – connections determine the speed of your internet. Some bandwidths are fixed and thus cannot be increased while you can widen others.
- Inadequate/old equipment, connections or wires - If you have outdated equipment, you wouldn’t expect it to measure up to current technology. Also, ensure that all your connections are appropriately configured less you want your internet speed to fluctuate.
What Speed is Required in a Household?
17Mbps
- It is perfect for light browsing and downloading in small households
- You can use it to stream TV
- Good for several internet users
- It takes 30 minutes to download an HD movie
38Mbps
- Ideal for multi-use
- Best for families with multiple devices
- It takes 15 minutes to download an HD film
- Easy to stream TV
76Mbps
- It is excellent for multi-user and most internet users streaming and download
- Ideal for households that value faster speeds
- It takes 8 minutes to download an HD movie
- Suitable for streaming online TV
Internet Speed Glossary
When understanding internet speeds and how they work, it’s helpful to arm yourself with some handy definitions:
- Bandwidth – Bandwidth measures the total number of frequencies, or capacity, a network connection can handle at any given moment. With more bandwidth, more data can be transferred through a specific network at a time. This is significant for determining how many devices can connect to the network at a time.
- Bit – Internet speed is measured in bits per second (bps). This is the smallest unit of computer information, so you’ll often see internet speeds referred to as megabits per second (Mbps).
- Download – This tells you how quickly information from external sources is received by your router.
- Latency – Latency measures the delay in data transfer, telling you how fast data gets from a source to its destination. Internet connection types vary considerably when it comes to latency. For instance, 100 Mbps with a fiber optic connection will have far fewer delays for tasks, such as Zoom meetings, than 100 Mbps with a satellite connection.
- Mbps – “Megabits per second” is how we gauge internet speeds. This number represents the bandwidth of an internet connection, which is how much data can be transferred each second.
- Upload – This tells you how quickly information from your network is sent to external networks.
- Wi-Fi – Wi-Fi offers a wireless internet connection, negating the need for devices to connect via hardware, such as an Ethernet cable.
FAQs
1. What is a good internet speed?
A good internet speed is one that can handle a high number of simultaneous connections without significantly slow internet speeds. This varies depending on the type of internet connection, but for most users, speeds of 25 Mbps or more are generally good.
2. What is more important upload or download speed?
The download and upload speeds of a computer are both important factors to consider when determining the overall performance of the system. The download speed is how quickly data can be transferred from the internet to the computer, while the upload speed is how quickly data can be sent from the computer to the internet. Generally, the download speed is more important than the faster upload speeds, as most people use their computers to consume content rather than produce it.
3. What is a good home Internet speed?
According to the FCC, the best Internet service provider for households with multiple devices and moderate to heavy internet use should offer download speeds of at least 12 Mbps. 25 Mbps are suggested to be the best internet speed for four or multiple devices. Homes with four or more users and four or more connected devices will undoubtedly require maximum download speeds of at least 25 Mbps.
4. Who has the fastest home Internet speed?
In the United States, Google Fiber offers the fastest average internet connection speed, closely followed by Verizon Fios. These two fiber internet service providers offer remarkable download, upload, and ping speeds. RCN, MetroNet, and Xfinity all offer respectable speeds on an average basis.
5. What is the Fastest Internet Ever?
178 terabytes of data per second.
Researchers in London have developed the world's fastest internet, capable of speeds of up to 178 terabits per second, or 178,000 gigabits per second. The speed is double that of any other system now in use on the planet and a fifth quicker than the previous world record of 150 Tbps held by a team in Japan.

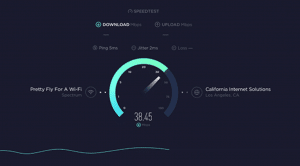

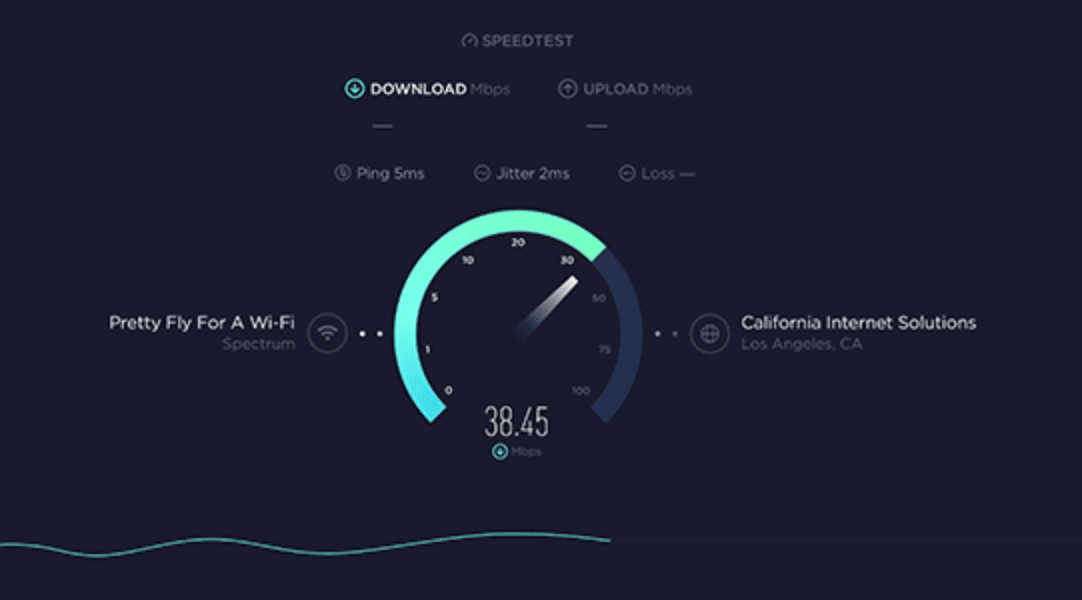

This article is really useful – we’ve also found quite a lot of home users here in the UK have ended up on congested 2.4GHz WiFi, particularly in dense populated areas, and can get a big speed boost from moving to 5GHz to take advantage of their connection