Table of Contents
What is a proxy?
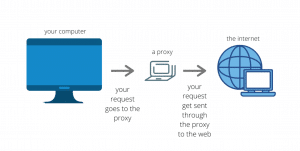
So what is a proxy? a proxy comes from the Latin to act in place of another. A proxy server acts as an intermediary for requests from a client’s IP address to a proxy server. Proxies are used in a number of ways but here we’re going to talk about them in terms of privacy and anonymity for Internet users. And in this context proxies mostly are used for surfing the web and downloading files to disguise the actual IP address of the client or user from the destination. A proxy server is popularly used on laptops, PCs, tablets, and phones (though phone data will still have privacy issues). People also often use a proxy server or proxy address for gaming as explained in our PS4 proxy server review. So, we hear you ask – What is my proxy server? , and – How to set up a proxy server?
Proxy servers are somewhat similar to VPNs like PrivacySharks but without encryption in most cases. VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) send all traffic on your operating system via an encrypted tunnel however web proxies on the other hand only forward the internet traffic of a specific single application.
There is no software to download and install to use a proxy. If you want a reliable proxy server network to change your own IP address and have optimal privacy while surfing the web, check out our Luminati proxy review. Or, look at the Storm Proxies Review , or RSocks Proxy Service Review, for some of the best providers out there. Often you just configure the application to use the proxy using the application’s own configuration and you can set up multiple applications to use a proxy server but it has to be set up per application. Moreover, if you encounter a ‘how to fix unable to connect to the proxy server‘ error, look into this article. So for example in Firefox we can go options -advanced – network and then settings and you’ll see this – 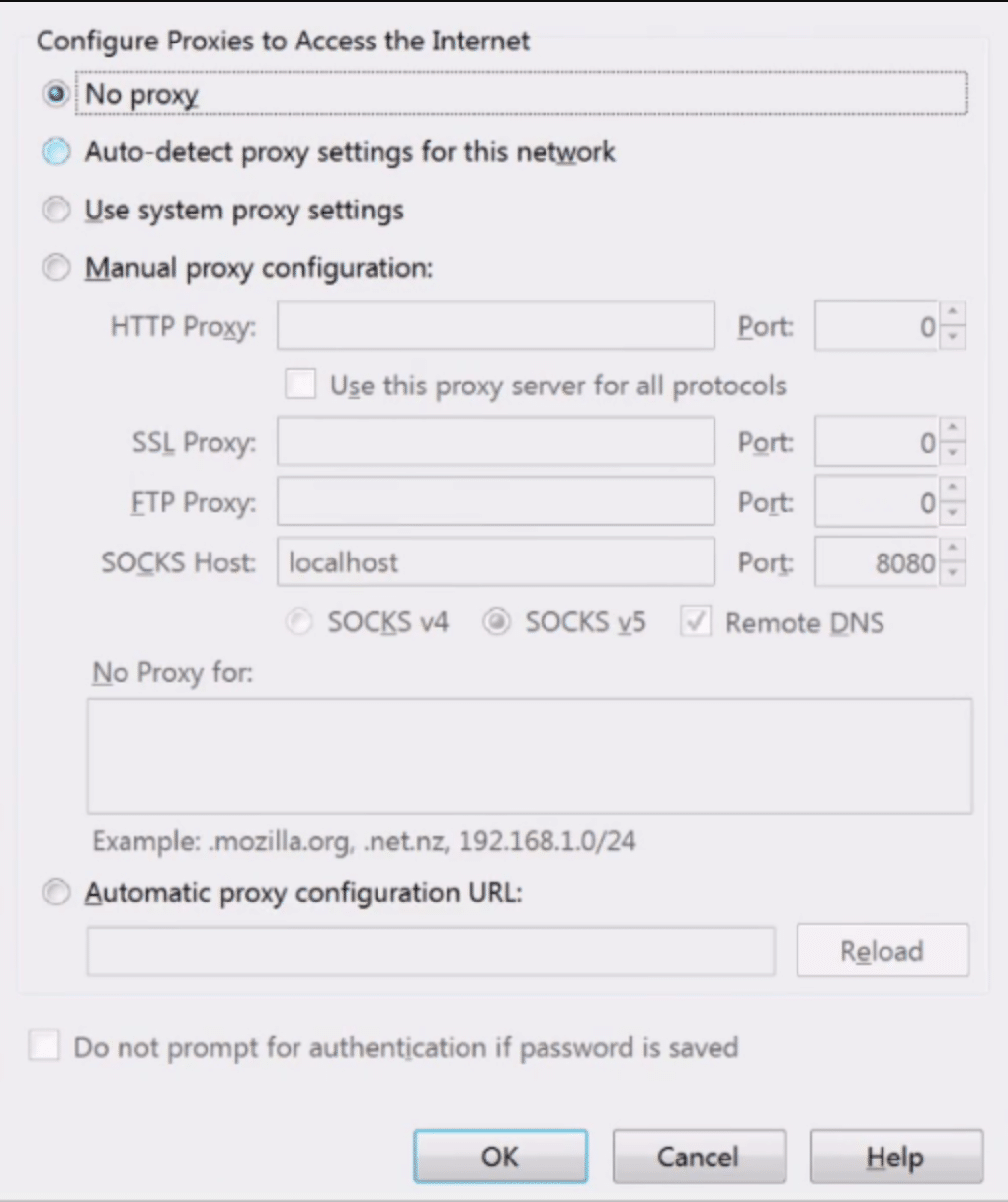
Here is where we set up the proxy settings for Firefox and other applications will have similar sort of settings in order to configure the application. To use a proxy server you need the IP address and the port of the proxy server and some will also have a username and password that you need to enter if it’s a private proxy or it’s a paid-for proxy. On the Settings dialog box, you’ll notice there’s actually a number of different proxies, we’ve got HTTP, we’ve got SSL, FTP, We’ve got SOCKS, SOCKSv4, SOCKSv5 so let’s go through these as well
The Different Types of Proxies
So let’s start with HTTP proxy, an HTTP proxy server understands and interprets the HTTP protocol only, and they are used mostly for surfing the web, and DNS resolution through them is supported. You can also check out if services designed for businesses can do the trick for individuals, too, in our Oxylabs Review.
Then we’ve got the SSL proxy or HTTPS proxy. This is the same but also supports SSL and or TLS between the proxy and the destination so make that clear, it’s between the proxy server and the destination. The SSL part can be misleading as there is no SSL encryption between the client and the proxy server but only between the proxy and the destination.
And then we have the FTP proxy which understands interprets the FTP protocol and is used obviously for FTP and you can get a proxy for pretty much any protocol you need but they won’t always be supported by your application like you can see, there is a limited set of protocols which it supports which is where SOCKS proxies come in as they are more flexible in what protocols that they can support.
Such proxies are different because they operate at a lower level of the ISO model than say for example HTTP or application-specific proxies and they try to be transparent to the user. Proxy servers are not protocoled specific so forward more protocols without a problem so for example you can put telnet, SSH, Tor, HTTP/HTTPS through SOCKS.
Here are other types of proxies that you can use for your privacy.
Transparent Proxy Server: It tells websites it is a proxy, but it still sends your IP address. Transparent proxies will identify themselves as a proxy, but not your IP address. It is also known as intercepting proxy server.
Anonymous Proxy Server: The server attempts to anonymize online browsing. It is basically a proxy system for proxy-aware apps. Anonymous proxy servers allow proxy users to browse the web anonymously.
Reverse Proxy Server: In contrast to a forward proxy, which is placed in front of clients, a reverse proxy is placed in front of web servers and forwards requests from browsers to the web servers. It operates by intercepting user requests at the web server’s network edge. It then makes requests to the origin server and gets responses from it.
Reverse proxies are an excellent choice for popular websites that must balance the load caused by a high volume of incoming requests. They may assist an organization in reducing bandwidth use by acting as another web server that manages incoming requests. The disadvantage is that reverse proxies may reveal the HTTP server architecture if an attacker manages to breach them. This implies that internal network managers who use a reverse proxy may need to beef up or relocate their firewall.
Forward Proxy Server: The most well-known kind of intermediate worker is the forward proxy server, which is accessed by the customer. An open or forward proxy server is a kind of intermediary that accepts web requests from clients and then browses destinations in order to collect the requested information.
Forward proxies are perfect for intranets requiring a single point of entry. In addition to providing IP address security, it allows straightforward administrative control. It may restrict a company’s ability to meet the needs of its individual users, however.
Distorting Proxy: A distorting proxy identifies itself as a proxy but hides its own identity and therefore IP address. This is accomplished by changing its IP address to an incorrect one.
When accessing the internet, a distorting proxy is an excellent choice for people wishing to hide their location. Using a proxy of this kind, you can appear to be logging into a different country while browsing, giving you the advantage of hiding your identity as well as that of the proxy. Your identity remains secure in spite of being associated with the proxy. Nevertheless, some websites automatically block distorting proxies, which could prevent an end-user from accessing websites.
High Anonymity Proxy Server: A high anonymity proxy is an anonymous proxy that takes anonymity to another level. In this case, your information is erased before the proxy attempts to connect to the target website.
The web server is best suited for users for whom anonymity is a necessity, such as employees who do not want their activities to be traced back to the organization. In contrast, some of these, especially the free ones, are decoys designed to trap users so they can steal their information.
Residential Proxy Server: The residential proxy gives you an IP address that corresponds to a specific, physical device. The web requests are then routed through that device.
Residential proxies are a great choice for users who need to verify the ads that appear on their website, so they can block suspicious or unwanted ads from competitors or bad actors. Alternative proxy options such as anonymous proxies are less trustworthy than residential proxies. However, they can cost more money to use, so users should carefully evaluate whether the extra cost is worth the benefits.
Difference Between Socks Proxy Versions
There are differences between the SOCKS versions as well and here we’ve got version 4 and version 5. Version 4 doesn’t allow remote DNS which means the proxy server cannot perform DNS lookups and it’s not ideal if you’re trying to hide where you’re going. SOCKS v4 also only supports TCP and not UDP. And then you have the SOCKS version 4A proxy server which actually isn’t configurable on here on Firefox, and this is a small enhancement on the v4 that allows the web proxy server to resolve domain names, and again it’s only TCP.
And then we move on to version 5 which adds on top of the features that the SOCKS 4A has and offers more choice in things like authentication, support for IPV 6 and UDP, and does support remote DNS. It can resolve DNS names through the proxy server which is what we need, now in special instances of an HTTPS proxy if the administrator has enabled the use of the connect method HTTPS proxies can behave like SOCKS proxies but only with HTTPS sites that support it. And an important note here to reemphasize there is no user to proxy encryption which means anyone observing the internet traffic between the user or this browser and the proxy can see connection details such as the destination IP address, your ISP (internet service provider), a hacker or a man in the middle will be able to see this. If the destination isn’t using SSL/TLS then the content of the outgoing and incoming traffic will also be observable.
Do Proxies Provide Privacy and Anonymity?
Proxy servers are generally far higher in the IP address of the client from the destination and they can work to bypass censorship in an environment that doesn’t examine the contents of the packet but if the consequences of getting caught are high then don’t use them at all. Web servers or proxy servers are faster than VPNs because there is no encryption with proxies, think of a proxy server as a basic form of hiding your IP address from the destination and not to be considered anonymous against moderate or serious adversaries.
If you plan to use or have access to multiple proxies I recommend the Foxy proxy Addon which enables you to quickly and easily set up different proxies and has all sorts of other useful features. If you’re using lots of proxies if you want to switch just a single proxy on and off then get yourself the Quick Java addon which has the proxy bottom where you can easily just switch on and off the proxy as you need thus saving you from having to go into the settings.
Paid Proxy Services
We discussed free proxies in our previous post, now about paid proxies. There are paid proxy services that are available from a number of companies such as BT guard, tor guard, and Foxy proxy just to name a few. I have no association and do not recommend any of those or don’t recommend them, they’re just examples and you pay maybe $45 per year to access those sorts of services. They are notably cheaper than VPN (Virtual Private Network) services but that’s because they don’t load the servers as much as a VPN server does because VPNs use encryption while proxies do not. Some proxy providers give you software to install but that’s not necessary if your application support proxies. These paid proxy services are mostly aimed at people downloading torrents however proxies are better at anonymizing you than nothing but are one of the weakest forms of a privacy service or anonymity service because of the lack of encryption.
The issues of trust are the same with proxy providers and you have no guarantee of what they are doing so even if a proxy provider state that they don’t log traffic you have no way of knowing if that is true. Plus when pushed by an adversary such as a nation-state will they roll over? Probably yes to keep their business just because they don’t keep logs doesn’t mean they can’t just switch them on. If they are coerced or subpoenaed or they just feel like doing it because they’re doing some sort of diagnostic it is trivial for a Nation-state adversary to monitor your activity with a proxy. It is even relatively trivial for a minor adversary to monitor your activity when you’re using proxies
FAQs
1. Do I need a proxy server?
Proxy servers can easily be used to boost network performance and save bandwidth by compressing traffic, caching files and web pages accessed by multiple users, and stripping advertisements from websites. Using a proxy server changes a user's IP address and helps free up valuable bandwidth on congested networks, allowing your team to connect to the internet quickly and easily and boosting up your internet usage and access blocked content.
2. Are proxy servers illegal?
Using a proxy server is not illegal. Proxies can be used for a variety of purposes, including enabling remote work, establishing a support system for users who are not connected to a specific network, protecting networks and Internet users by changing their IP address using a proxy service to be safe from malicious content, and streaming online content from outside a country.
3. Why do hackers use proxy servers?
A proxy server decreases the likelihood of a breach. Proxy servers act as a buffer because they can communicate with the internet and relay a web request from computers on the outside of the network. While hackers may gain access to your proxy server, they will have difficulty reaching the server that actually runs the web software that stores your data.
4. How safe are proxies?
While proxies conceal your IP address and only the proxy's IP address (internet protocol address) can be seen publicly, proxy servers do not conceal any of your data as it traverses between servers. This is because it is frequently sent in an unencrypted format. This means that any information you send could be viewed by malicious actors who intercept your data (login information, baking details, etc.)
5. Is using a proxy server faster?
Yes, using a proxy server can speed up your Internet connection, but the increase will be minimal. You can rest assured that proxies will not affect the performance of your computer. This occurs because the speed of your Internet connection is typically slower than the proxy's datacenter.
6. What is caching proxy server?
This is a type of Internet/network caching technique that allows a proxy server or servers to store recent and frequent website / webpage requests and data requested by one or more clients. Caching proxies servers can also be referred to as a web proxy cache.
7. What is the difference between proxy and Reverse Proxy?
A forward proxy server, in the conventional sense, enables many clients to route traffic to an external network. For example, a company may use a proxy to route and filter employee traffic to and from the public Internet. On the other hand, a reverse proxy forwards traffic on behalf of many servers.